TL;DR: Enhanced (color-treated) diamonds give vivid hues and value-for-size through post-mining treatments, while natural diamonds are prized for rarity, natural color, and long-term resale — both have places in modern rings. This guide covers treatments, visual differences, certification, value, buying checklists, care, comparison tables, case studies, and FAQs to help you decide with confidence.
Table of Contents
- Hook: Why this matters in 2025
- Definitions — What we mean by 'enhanced' & 'natural'
- How enhancement treatments work
- Visual differences and quick tests
- Price & value comparison
- Certification & reporting
- A practical buying checklist
- Best ring settings for each type
- Care & maintenance
- Case studies & real examples
- Pros & Cons
- Comparison table
- Infographic placeholders
- FAQs
- Final recommendation & CTAs
Hook — Why this matters right now
In 2025 the diamond market is more varied than ever: ethical concerns, lab-grown options, and advanced post-mining treatments (color enhancement, HPHT, irradiation, fracture filling) mean shoppers must understand what they buy. For rings — often emotional, frequently expensive — knowing whether a diamond is enhanced or naturally colored impacts price, care, and long-term value. FancyDiamondJewels offers both enhanced and natural color diamonds across its catalog, and this guide helps you choose what fits your priorities. For product inspiration and real examples, see FancyDiamondJewels’ featured ring collections and product listings which include explicit treatment labels.
Definitions — Enhanced vs Natural
What we mean by 'Enhanced' diamonds
“Enhanced” refers to natural diamonds that have had their color and/or clarity improved through human-applied treatments after mining. Common processes include irradiation, high-pressure high-temperature (HPHT) treatment, laser drilling, and fracture filling. These treatments can dramatically alter the appearance and market price of the diamond without changing the basic carbon crystal structure.
What we mean by 'Natural' diamonds
By “natural” we mean diamonds whose current color and clarity are the result of geological processes, not post-mining artificial treatments. Natural colored diamonds (fancy yellow, blue, pink, brown, gray, black, etc.) are graded and valued for their innate rarity and stability.
How enhancement treatments work — step-by-step
HPHT (High Pressure, High Temperature)
- Diamond is placed in a press at extreme pressure & temperature.
- Crystal lattice defects are repaired; a brown diamond may become colorless or change shade.
- Result: stable color changes that often survive normal wear and cleaning.
Irradiation + Annealing
- Diamond exposed to controlled particle irradiation (electrons, neutrons).
- Color centers are created; annealing stabilizes new color (common for blues & greens).
- Result: vivid colors but sometimes require careful disclosure and labeling.
Fracture filling & clarity enhancements
- Small surface-reaching fractures are filled with glass-like substances.
- Improves apparent clarity but can be sensitive to heat/chemicals.
- Requires lab disclosure — not considered permanent in all contexts.
Many FancyDiamondJewels product pages clearly list whether a stone is “Color Enhanced Natural” or “Untreated 100% Natural” in product specs — always check the product detail before purchasing.
Visual differences & quick tests
Some visual cues are helpful but not definitive without a lab report:
- Uniform color: Treated stones—especially dyed or irradiated—may show very consistent color under magnification.
- Surface flash: Fracture fills can produce flash or “rainbow” reflections when viewed at angles.
- Price vs intensity: Extremely saturated colors at a low price point may indicate enhancement.
At-home quick checks
- Use a loupe: look for filled fractures and unusual flash.
- Expose to heat (careful): many fracture fills are sensitive to household soldering — but do not attempt destructive testing on your own ring.
- Request documentation: the most reliable test is a gemological lab report or seller-disclosed treatment info.
Price & value comparison: what to expect
General rules (market averages):
- Natural, untreated fancy-colored diamonds (pink, blue) often command the highest premiums due to rarity.
- Enhanced (color-treated) diamonds typically cost less per carat than naturally fancy stones of the same apparent color intensity.
- Plain colorless natural diamonds retain value better over time than treated stones; resale expectations differ widely.
FancyDiamondJewels shows a wide range of pricing for treated (color enhanced) products and natural stones in their catalog — compare product detail pages to see treatment notes and price differences.
Certification & reporting — what to demand
Always get a written report that includes treatment disclosure. For natural and fancy-color diamonds, insist on a recognized lab report (GIA, IGI, or other reputable lab) that states whether the stone is treated. If a report is not practical (e.g., for very small accent stones), get a clear seller disclosure and return policy in writing.
Red flags in documentation
- No mention of treatment where the color is unusually strong for price.
- Ambiguous language such as “may have been treated.”
- Absence of a lab report when purchasing a premium-colored stone.
A practical buying checklist (printable)
| Item | Why it matters | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment disclosure | Impacts care/resale | Get in writing |
| Lab report | Authenticity & grading | Request GIA/IGI or equivalent |
| Return policy | Try on, inspect at home | Confirm 14–30 day returns |
| Setting compatibility | Heat-sensitive fills can be damaged during repair | Ask jeweler before resizing |
| Long-term value | Investment expectations | Decide if resale matters |
Best ring settings for each type
Enhanced (color-treated) diamonds — recommended settings
- Bezel & halo settings: protect the girdle and reduce exposure to knocks.
- Low-profile settings: minimize the chance of hitting fracture-filled areas.
Natural colored diamonds — recommended settings
- Prong and solitaire settings to maximize light exposure.
- Open gallery settings for larger natural fancy colors to showcase hue.
Care & maintenance — do’s and don’ts
Enhanced diamonds
- Check with seller before ultrasonic cleaning — some treatments (fracture filling) are sensitive.
- Avoid high-heat repairs unless the stone is removed.
- Store separately to avoid scratching other jewelry.
Natural diamonds
- Most natural diamonds are durable and safe with standard jewelers’ care.
- Periodic professional cleaning and inspection recommended.
Case studies — three real examples from FancyDiamondJewels
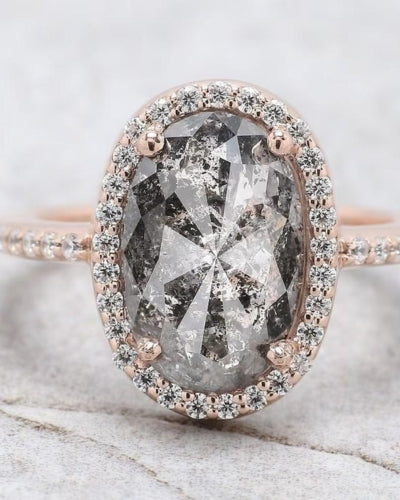
Case Study 1 — Color Enhanced Rough Blue Diamond Ring
Product listing: a rough blue diamond ring explicitly labeled as “Color Enhanced Natural.” The product spec lists diamond weight, clarity, and treatment, allowing buyers to evaluate cost vs natural blues. This is an example of how enhancement enables accessible blue tones at lower price points.
Rough blue color enhanced diamond ring













Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.